Based on population, a Black person was 2.7x as likely and a Latinx person was 1.6x as likely to be killed by police as a White person in America from 2013-23.
Key Findings
12,365 Killings by Police
324,152 civilian complaints of police misconduct
Only 1 in every 7 complaints were ruled in favor of civilians from 2016-2022.
92,812,897 arrests made
Police in America made 13x as many arrests for low level offenses as for violent crimes from 2013-2023.
United States Police Department Scores
Rankings are based upon a 0 to 100 percentage scale. Departments with higher scores use less force, make fewer arrests for low level offenses, solve murder cases more often, hold officers more accountable and spend less on policing overall.
Overall Scores for Depts where We Have Obtained the Most Data.
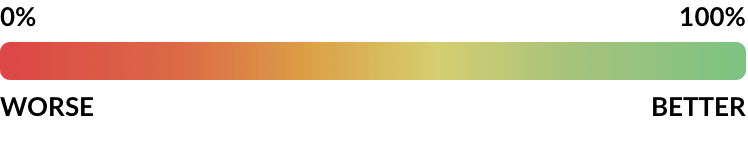 Tap "show more" to see extended list
Tap "show more" to see extended list
* An asterisk indicates this location did not publish enough data to evaluate. Click below to add data to the Scorecard.
About This Scorecard
This is the first nationwide evaluation of policing in the United States. It was built using data from state and federal databases, public records requests to local police departments, and media reports. While police data is never perfect, and there are additional indicators that still need to be tracked, the Police Scorecard is designed to provide insight into many important issues in policing.
Police Scorecard is an independent 501(c)(3) organization, learn more about our team here. If you have feedback, questions about the project, or need support with an advocacy campaign, contact our Founder, Samuel Sinyangwe.
Use this Scorecard to identify issues within police departments that require the most urgent interventions and hold officials accountable for implementing solutions. For example, cities with higher rates of low level arrests could benefit most from solutions that create alternatives to policing and arrest for these offenses. In cities where police make fewer arrests overall but use more force when making arrests, communities could benefit significantly from policies designed to hold police accountable for excessive force. And cities where complaints of police misconduct are rarely ruled in favor of civilians could benefit from creating an oversight structure to independently investigate these complaints.
Here's how to start pushing for change
- Contact your Mayor and Police Chief, share your scorecard with them and urge them to enact policies to address the issues you've identified:
-
Look up your state and federal representatives below, then tell them to take action to hold police accountable in your community.
Find Elected Officials
Join a team of researchers, students, data scientists, activists and organizers working to collect, analyze and use data for justice and accountability.
Create data visualizations and content that raises awareness about solutions to the issues identified by the data.
What's Next
Step 1: COMPLETED

Obtain data on 100 California cities. Refine methodology in response to feedback from communities, researchers and local officials.
Step 2: COMPLETED

Expand to every major law enforcement agency in America and include additional indicators such as police budgets and jail incarceration.
Step 3: IN PROGRESS

Inform data-driven solutions nationwide. Update as new federal, state and local data are collected. Track progress and hold cities accountable to results.